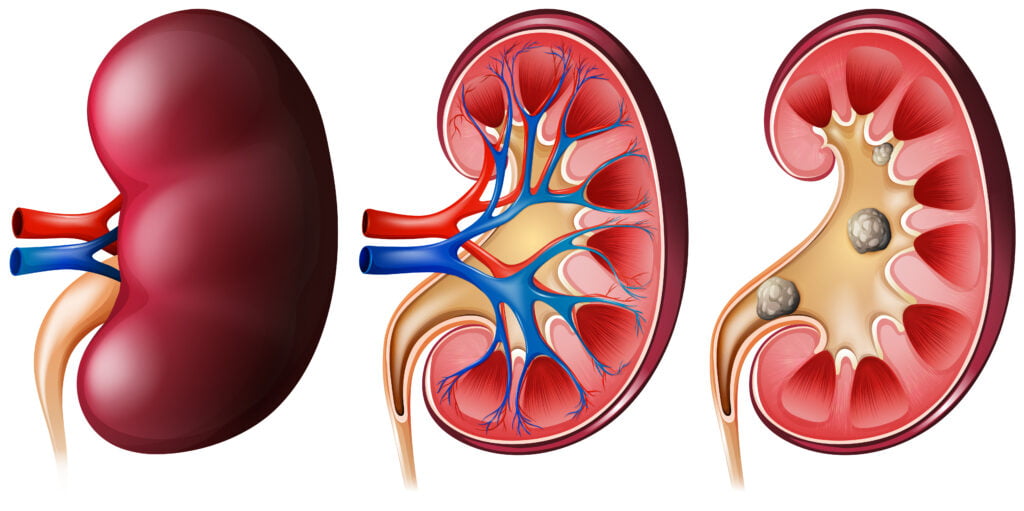
Kidney stones, medically known as renal calculi, are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. They can cause immense pain and discomfort when they move through the urinary tract. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about kidney stones – from symptoms and causes to treatment options and prevention strategies.
I. Kidney Stone Symptoms
- Sharp Pain: One of the most common symptoms of kidney stones is intense, sharp pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen.
- Discolored Urine: Urine may appear pink, red, or brown due to the presence of blood.
- Frequent Urination: You may feel the urge to urinate more often, accompanied by pain or discomfort.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals experience nausea and vomiting as a result of stone pain.
II. Kidney Stone Causes
- Dehydration: Dehydration can cause concentrated urine, which raises the possibility of stone development.
- Dietary Factors: Consuming foods high in oxalate, calcium, or purines can contribute to stone formation.
- Family History: Genetics can play a role in predisposing individuals to develop kidney stones.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like hyperparathyroidism or urinary tract infections can increase the risk.
III. Kidney Stone Pain
- Location: The pain typically starts in the back or side and may radiate to the lower abdomen and groin as the stone moves.
- Intensity: The pain can vary in intensity from mild discomfort to excruciating agony, often described as one of the most severe pains one can experience.
- Duration: The duration of pain can vary depending on the size and location of the stone.
IV. Kidney Stone Treatment
- Fluid Intake: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out the stones from the urinary tract.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or prescription-strength analgesics can alleviate discomfort.
- Medication: Certain medications like alpha blockers or calcium channel blockers may help relax the muscles in the urinary tract, facilitating stone passage.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): This non-invasive procedure uses shock waves to break up the stones into smaller pieces, making them easier to pass.
V. Kidney Stone Surgery
- Ureteroscopy: A thin, flexible scope is passed through the urethra and bladder to the ureter, where the stone is located, and then removed or broken up with a laser.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): This procedure involves making a small incision in the back to access the kidney directly and remove the stone.
VI. Kidney Stone Pain Location
- Back and Side: Pain often originates in the back or side, near the location of the affected kidney.
- Lower Abdomen: As the stone moves through the urinary tract, the pain may radiate to the lower abdomen and groin.
VII. Kidney Stone Removal
- Natural Passage: Small stones may pass through the urinary tract naturally with increased fluid intake and pain management.
- Surgical Intervention: Larger stones may require surgical procedures like ureteroscopy or PCNL for removal.
VIII. Kidney Stone Symptoms in Women
- Similar Symptoms: Women experience similar symptoms to men, including pain, discolored urine, nausea, and vomiting.
- Additional Concerns: Pregnancy and anatomical differences in the urinary tract may pose additional challenges in diagnosis and treatment.
IX. Kidney Stone Removal Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Options: Advances in surgical techniques have led to less invasive procedures with shorter recovery times.
- Risk Factors: Your doctor will assess factors such as stone size, location, and overall health to determine the most appropriate surgical approach.
X. Kidney Stone Diet
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake, especially water, is crucial for preventing stone formation.
- Moderation: Limiting intake of foods high in oxalate, sodium, and animal proteins can reduce the risk of stone recurrence.
XI. Kidney Stone Pain Relief
- Heat Therapy: The affected area can benefit from applying heat to help relax muscles and reduce pain.
- Positioning: Changing positions or lying down on the side of the pain may provide relief.
XII. Kidney Stone Medication
- Pain Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids may be prescribed to manage pain.
- Alpha Blockers: These medications relax the muscles in the ureter, making it easier for stones to pass.
XIII. Kidney Stone Stent
- Placement: In some cases, a small tube called a stent may be placed in the ureter to facilitate urine flow and relieve obstruction caused by the stone.
- Temporary Measure: Stents are typically temporary and may be removed once the stone has passed or been treated.
XIV. Kidney Stone Prevention
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain urine volume and prevent stone formation.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting processed foods and sodium intake.
XV. Kidney stone doctor
The diagnosis and treatment of kidney stones is the focus of a urologist, sometimes known as a kidney stone doctor. These healthcare professionals specialize in treating disorders of the urinary tract, including stone production and transit. They are able to precisely determine stone size, location, and composition by using modern diagnostic techniques like imaging tests and urine analysis. Aside from minimally invasive procedures like ureteroscopy or shock wave lithotripsy, treatment options may also include lifestyle changes and drugs to help the stone pass through. Larger stones or situations of blockage might require surgery.
Summary
In summary, kidney stones can cause significant pain and discomfort, but with proper understanding of symptoms, causes, and treatment options, individuals can effectively manage and prevent their recurrence. If you suspect you have kidney stones or are experiencing symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate assessment and care.
Patient Precautions
| Precautions | Dietary Adjustments |
|---|---|
| Increase water intake | Limit intake of salt and sodium-rich foods |
| Avoid dehydration | Reduce consumption of oxalate-rich foods |
| Maintain a healthy weight | Include calcium-rich foods in moderation |
| Monitor urine color and volume | Limit animal protein intake |
| Follow prescribed medication regimens | Incorporate fruits and vegetables daily |